which ones are isoelectric
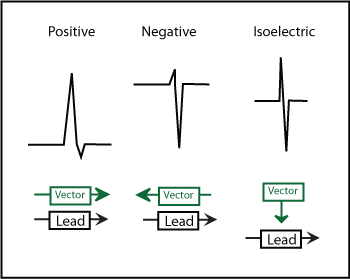
In the context of electrocardiography (ECG), isoelectric leads are those that exhibit a net amplitude of zero, meaning that the electrical activity in these leads indicates equal positive and negative deflections. Here are the leads commonly identified as isoelectric:
-
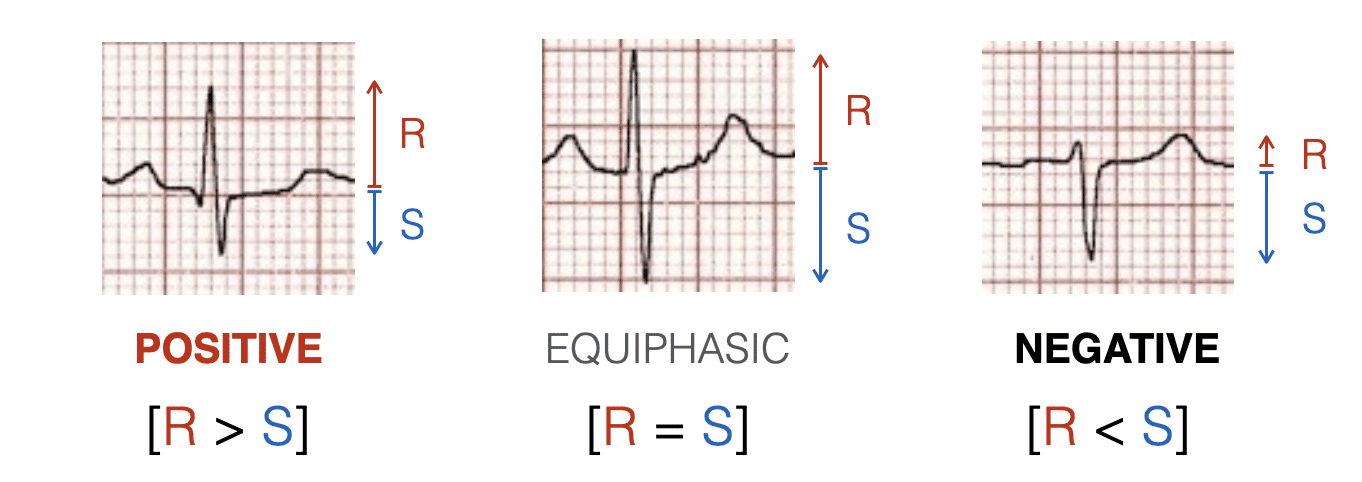
Lead III: According to the Deranged Physiology article, lead III is often described as the lead with the most isoelectric trace where the Q and R waves are of the same height. You can find more information in their documentation here: The QRS Axis: the Isoelectric Lead Method.
-
Lead aVL: The DVM 360 article states that in some ECG analyses, lead aVL may also be identified as isoelectric. It is positioned perpendicular to lead II, which generally has mostly positive deflections. More details can be found in their tutorial: Skills Laboratory: How to determine and interpret the mean electrical axis.
-
General Concept: In general, any lead where the electrical activity is oriented at 90 degrees to the lead will be considered isoelectric. This is explained in the Teaching Medicine tutorial, which discusses the relationship between lead angles and their isoelectric nature: Axis - The Isoelectric lead.
Thus, leads III and aVL are commonly noted as isoelectric in various contexts. Identifying which lead is isoelectric in a specific ECG can be essential for accurate readings and diagnosis. You can find further clarification on the definitions of isoelectric leads in sources like the NCBI Bookshelf: Electrical Right and Left Axis Deviation.
Sources
Related Questions
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.
