What Sections Should Be In A Project Charter Vs Project
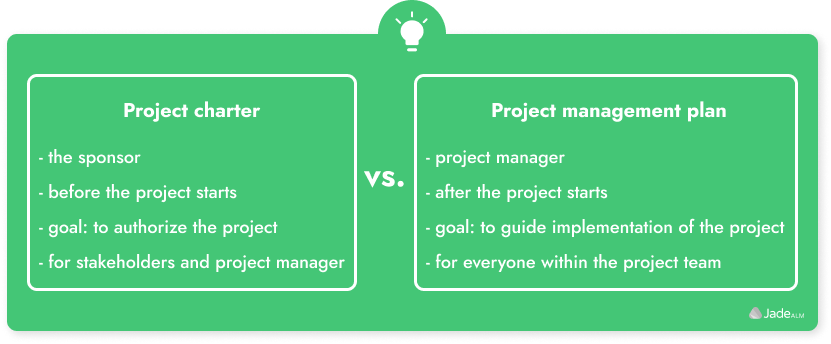
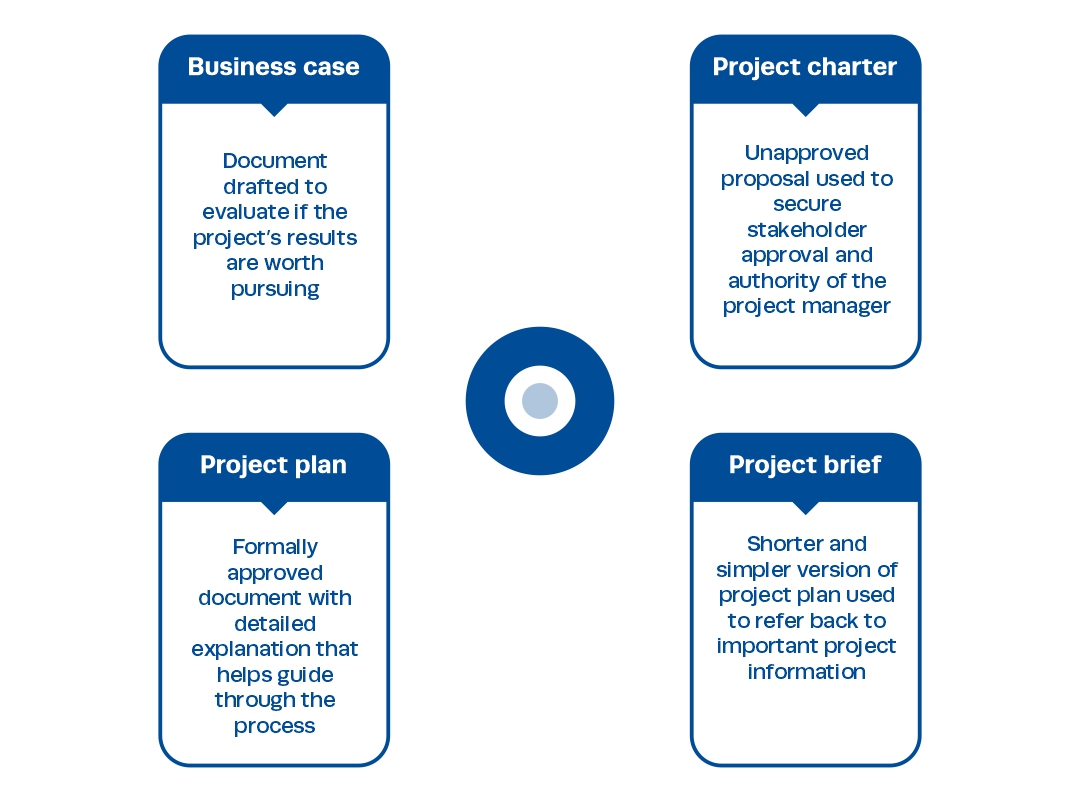
A project charter is a sales document that presents the proposed project idea to stakeholders. It acts as a reference point throughout the project lifecycle while the project plan manages day-to-day project management. The Identity and Access Management Modernization Program aims to modernize the University's systems. The project management framework provides guidance for project phases, and the project charter acts as a "contract" between stakeholders, the project team, and beneficiaries. It includes project constraints, goals, budget, and the appointment of a project manager. The Employment Department's Modernization Program transforms its business processes, and the IT Project Manager Guide offers guidance for project managers.
In a project charter for an IT modernization project involving legacy enterprise identity access management systems, the following sections are typically included:
-
Project Purpose and Justification: This section outlines the reasons for the project and the benefits it is expected to deliver to the organization. It provides clarity on the necessity of modernizing the legacy systems.
-
Project Objectives: Here, the specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives of the project are defined. This section should clearly articulate what the project aims to achieve in terms of modernizing the identity and access management systems.
-
Scope and Deliverables: This section outlines the boundaries of the project and the specific products, services, or results that the project is expected to deliver. It helps in defining what will be modernized and what will be the expected outcomes.
-
Stakeholder Identification and Analysis: Identifying the key stakeholders and analyzing their expectations, influence, and involvement in the project is crucial for effective management and communication.
-
Project Management Approach: This section outlines the general approach to be taken in managing the project. It may include the project lifecycle, project organization, and key management processes.
-
Assumptions and Constraints: Listing the key assumptions and constraints under which the project will be executed helps in managing expectations and understanding potential limitations.
-
Risks and Issues: Identifying potential risks and issues that may affect the project and its objectives is essential for effective risk management and mitigation.
In contrast, the project management plan for this type of project would include sections such as:
-
Project Organization: Detailing the project team structure, roles, and responsibilities.
-
Communication Plan: Outlining the communication channels, frequency, and stakeholders involved in the project.
-
Resource Management Plan: Defining how resources will be allocated, managed, and utilized throughout the project.
-
Schedule and Milestones: Presenting the project schedule, milestones, and dependencies to ensure timely delivery.
-
Quality Management Plan: Describing the approach to ensuring quality throughout the project and modernization process.
-
Risk Management Plan: Outlining the strategies for identifying, assessing, and managing risks throughout the project lifecycle.
-
Change Management Plan: Detailing the approach to managing changes, including changes to requirements, scope, and resources.
These are of course indicative sections and the specific content within each would need to be tailored to the unique requirements of the IT modernization project involving legacy enterprise identity access management systems.
Sources
Related Questions
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.
