what is hepatoma
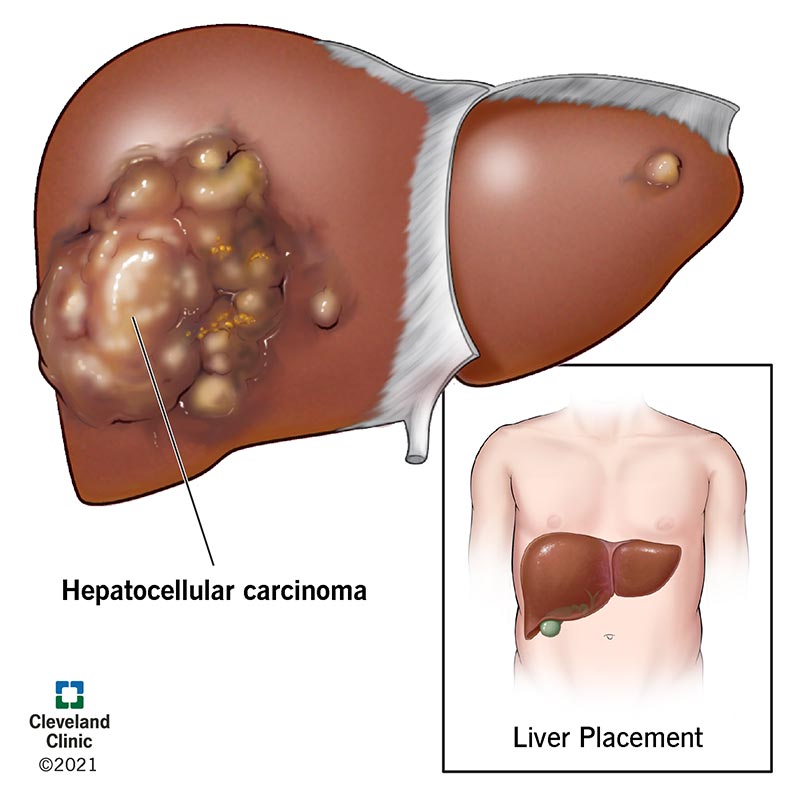
Hepatoma, also known as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is primarily defined as a malignant tumor that originates in the liver. This type of cancer is significant because it is the most common form of primary liver cancer, accounting for more than 90% of liver tumors (Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559177/).
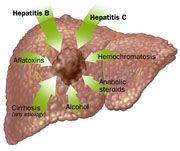
Individuals at higher risk for developing hepatoma include those with chronic liver diseases, such as hepatitis B or C, and conditions that lead to cirrhosis. Symptoms of HCC may not be evident in the early stages, but as the cancer progresses, patients might experience abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and swelling in the abdomen (Source: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hepatocellular-carcinoma/cdc-20354552).
Early detection plays a critical role in treatment options, which may include surgery, liver transplantation, chemotherapy, or targeted therapies. The prognosis can improve significantly if the cancer is caught early and properly managed (Source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21709-hepatocellular-carcinoma-hcc).
For additional information about the definition and medical nuances of hepatoma and its implications, you may refer to sources like Merriam-Webster and the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Dictionary of Cancer Terms (Source: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/hepatoma; https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/hepatoma).
In summary, hepatoma is a serious form of liver cancer that necessitates prompt medical attention and multidisciplinary management to optimize treatment outcomes.
Sources
Related Questions
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.
