what is diffirence between 529 college planning and IUL investng
The difference between 529 college planning and Indexed Universal Life (IUL) investing for students primarily revolves around purpose, tax implications, flexibility, and costs. Below is a detailed summary of these two financial planning options:
529 College Savings Plan
-
Purpose: The primary goal of a 529 plan is to help families save for future education costs. Funds in a 529 plan can be used for qualified education expenses, such as tuition, room, and board.
-
Tax Advantages: Contributions to a 529 plan grow tax-deferred, and withdrawals for qualified education expenses are tax-free at the federal level (and in many cases, state level). This makes it a very tax-efficient way to save for college.
-
Restrictions: The funds must be used for qualified education expenses; otherwise, withdrawals are subject to taxes and potential penalties. The plan is aimed specifically at saving for education, which limits its use for other financial needs.
-
Growth Potential: 529 plans typically invest in a variety of mutual funds and investment portfolios, which can offer solid growth potential over time, especially when considering the time horizon until college expenses are incurred.
-
Account Ownership: The account owner retains control over the funds, and the beneficiary can be changed if needed, providing some flexibility in who can use the funds.
Indexed Universal Life (IUL) Insurance
-
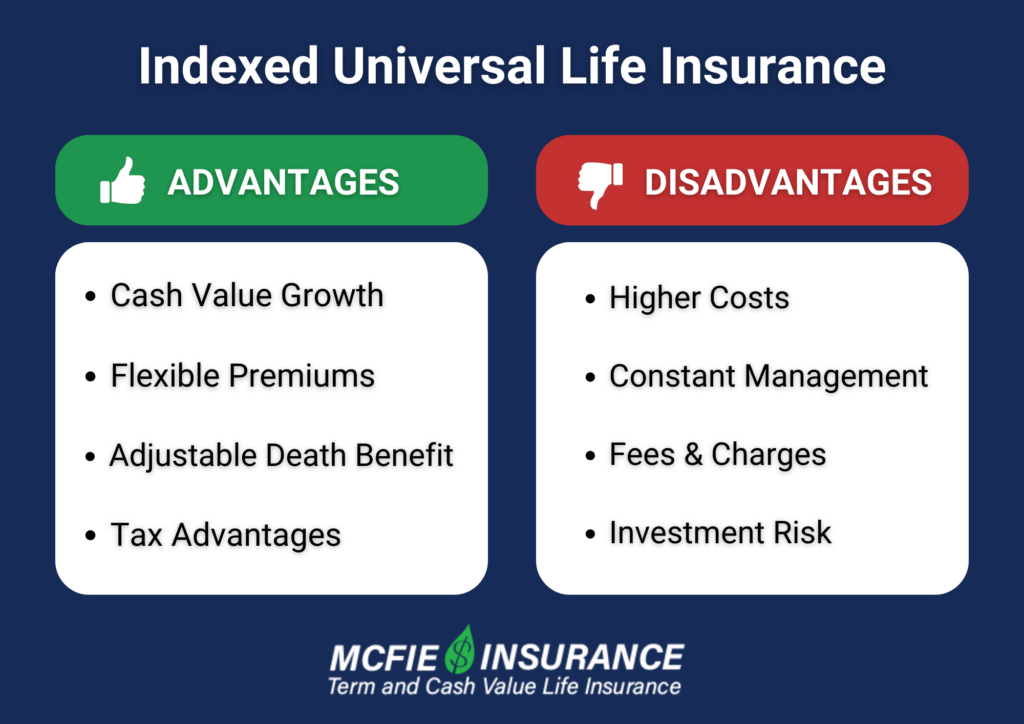
Purpose: IULs are permanent life insurance policies that include an investment component. While they can provide a death benefit, they also allow policyholders to accumulate cash value, which can be accessed during the policyholder's lifetime.
-
Flexibility: One of the key advantages of IULs is their flexibility. Unlike 529 plans, funds can be used for any purpose—including education—but they may not offer the same tax advantages as 529 plans for education-related expenses.
-
Tax Considerations: The cash value in an IUL grows tax-deferred, and policyholders can take loans against the cash value. However, if the policy is surrendered, or if loans are not repaid, there may be tax implications.
-
Cost: IULs can be more expensive than 529 plans due to insurance costs associated with the policy. They often produce lower returns compared to traditional investment options, which can be a disadvantage for investment growth.
-
Long-term Financial Planning: IULs can be a component of a broader financial plan, offering insurance coverage while also serving as an investment vehicle.
Summary
In summary, a 529 college savings plan is specifically designed for education savings with tax advantages, while an Indexed Universal Life insurance policy provides flexible investment options with insurance coverage. If the primary goal is saving for college, a 529 plan may be a better choice due to its tax benefits and focused purpose, whereas an IUL offers broader financial flexibility at a potentially higher cost.
For further reading on this topic, you can explore articles from Investopedia, Policy Engineer, and Nasdaq.When considering saving for education, understanding the differences between a 529 college savings plan and Indexed Universal Life (IUL) insurance investing is crucial for making informed decisions. Here’s a detailed comparison:
529 College Savings Plans
-
Purpose: A 529 plan is specifically designed for education savings. It provides a dedicated account to save for qualified higher education expenses, such as tuition and fees, room and board, and other associated costs.
-
Tax Benefits: Contributions to a 529 plan grow tax-deferred, and withdrawals used for qualified education expenses are tax-free at the federal level. Many states also offer tax deductions or credits for contributions made to a 529 plan, adding to the financial benefits. More details can be found in articles from Investopedia and Saving for College.
-
Usage Restrictions: Funds in a 529 plan must be used for qualified education expenses. If the funds are used for non-qualified expenses, taxes and penalties may apply. This can be a significant limitation for flexibility.
-
Control: The account owner retains control over the funds, including deciding when and how much to withdraw for educational purposes. This is particularly beneficial for parents or guardians managing the savings.
-
High Contribution Limits: 529 plans typically allow for significant contributions, making them suitable for comprehensive education savings.
Indexed Universal Life (IUL) Insurance
-
Purpose: IUL insurance is primarily a life insurance product that includes a cash value component which can be accessed during the policyholder’s lifetime. It’s not exclusively intended for college savings, but it can be used for that purpose.
-
Flexibility: Unlike a 529 plan, IULs offer more flexibility in accessing cash value, which can be used for various financial needs, not just educational expenses. This allows policyholders to cover a broader range of financial situations.
-
Tax Treatment: The cash value grows tax-deferred, and withdrawals may be taken tax-free up to the policy's basis. However, if the policy is surrendered, or if loans are taken against the cash value, there could be tax implications. Further information can be reviewed in detail at Everly Life.
-
Cost: IULs can be expensive, incorporating insurance costs that may decrease the overall return when compared to more straightforward investment options. It’s essential to evaluate the cost-to-benefit ratio when considering IULs as a savings mechanism for education.
-
Dual Benefits: One of the notable features of IUL policies is that they provide life insurance protection, which could serve as an additional benefit for families seeking insurability for their dependents.
Summary
Choosing between a 529 college savings plan and IUL investing depends largely on your objectives—if you want a targeted education fund with tax advantages, a 529 plan is likely a better fit. Conversely, if you prefer more flexibility and the additional benefit of a life insurance policy, an IUL may be worth considering but may come with higher costs. Thus, understanding the distinct features, benefits, and limitations of each option is crucial before making a decision.
For more insight into this comparison, detailed articles such as those from Bankrate and Nasdaq provide comprehensive information.When considering the differences between a 529 College Savings Plan and Indexed Universal Life (IUL) insurance for students, there are several important factors to explore. Both options serve as means of saving for future educational expenses, but they function in significantly different ways. Here’s a detailed comparison:
529 College Savings Plan
Overview: A 529 Plan is a tax-advantaged savings plan designed specifically for future education expenses. Contributions to a 529 plan grow tax-deferred, and withdrawals are tax-free when used for qualified educational expenses.
Benefits:
- Tax Advantages: Earnings grow tax-deferred, and withdrawals for qualified education expenses are tax-free. Many states also offer tax deductions or credits for contributions.
- High Contribution Limits: 529 plans generally allow for high contribution limits, making them a robust option for saving.
- Flexible Investment Options: 529 plans typically offer various investment portfolios from which you can choose.
- Direct Control: The account owner maintains control over the funds.
Drawbacks:
- Restrictions on Use: Funds must be used for qualified education expenses; otherwise, there may be penalties and taxes on earnings. This restricts the flexibility of use compared to other savings vehicles.
- Impact on Financial Aid: 529 plans may be counted as assets in financial aid calculations, potentially affecting eligibility.
- Limited Investment Control: Once in a 529 plan, investment options are typically limited to those offered by the plan provider.
For more in-depth details on the 529 plan, see Investopedia's Overview.
Indexed Universal Life (IUL) Insurance
Overview: IUL is a type of permanent life insurance that includes a cash value component. The cash value can be linked to a stock market index to potentially offer higher returns while also providing a death benefit.
Benefits:
- Flexible Use of Funds: Unlike 529 plans, IUL cash value can be accessed at any time and used for a variety of expenses, including education, without specific penalties for non-educational use.
- Death Benefit: An IUL provides a death benefit, which can offer peace of mind for parents planning for their children’s future.
- Tax Advantages: Similar to 529 plans, the growth in cash value is tax-deferred, and policyholders can access funds through loans or withdrawals, typically with favorable tax treatment.
Drawbacks:
- Complex Structure: IULs are often more complex, with various fees, caps on returns, and terms to understand.
- Costs: IULs can be more expensive upfront compared to contributing to a 529 plan due to insurance costs and premiums.
- Uncertain Returns: Though they can provide high returns tied to indices, returns aren’t guaranteed, and there may be caps on potential earnings (often limiting the growth).
For a deeper look at IUL, you may refer to Investopedia's Pros and Cons and SmartAsset's Comparison.
Conclusion
In summary, the choice between a 529 College Savings Plan and an Indexed Universal Life insurance plan depends largely on personal financial goals and preferences. If the focus is strictly on saving for education with tax benefits, a 529 plan might be preferable. However, if more flexibility for fund usage and a death benefit are desired, an IUL could be a viable alternative. It’s crucial to weigh each option’s pros and cons carefully based on individual circumstances.
Sources
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Pros-and-cons-indexed-universal-life-insurance_final-1b83c0fd52154eb69edd47f99ab8927a.png)
Related Questions
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.
