What Is Copd And What Are The Common Comorbidities Associated
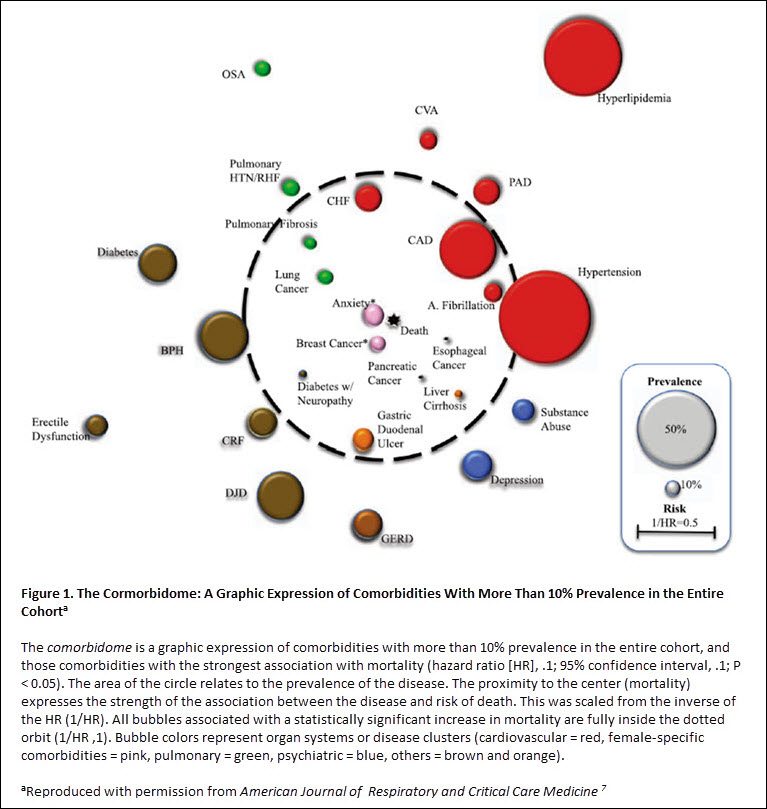
The texts highlight the prevalence and impact of comorbidities in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Comorbidities refer to other chronic medical conditions, such as coronary artery disease, diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, and muscle weakness, that are commonly present in patients with COPD. The presence of comorbidities is associated with systemic inflammation and can worsen conditions like ischemic heart disease, heart failure, and lung disease. Notably, COPD is associated with a higher prevalence of comorbidities compared to other diseases, and certain comorbidities, like hypertension and dyslipidemia, are more frequent in patients with severe COPD. Furthermore, comorbidities like pulmonary artery disease, malnutrition, and systemic venous thromboembolism can directly result from COPD. In order to effectively manage COPD, comorbidities should also be taken into consideration.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. This condition is characterized by increasing breathlessness.
Common comorbidities associated with COPD include:
- Coronary artery disease
- Diabetes mellitus
- Osteoporosis
- Muscle weakness
- Ischemic heart disease
- Heart failure
- Hypertension
- Dyslipidemia
- Pulmonary artery disease
- Malnutrition
- Systemic venous thromboembolism
The presence of these comorbidities can exacerbate the impact of COPD, leading to systemic inflammation and a higher prevalence of certain conditions in patients with severe COPD. It's essential to consider and manage these comorbidities effectively alongside COPD treatment.
Sources

Related Questions
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.
