what about the pancrease
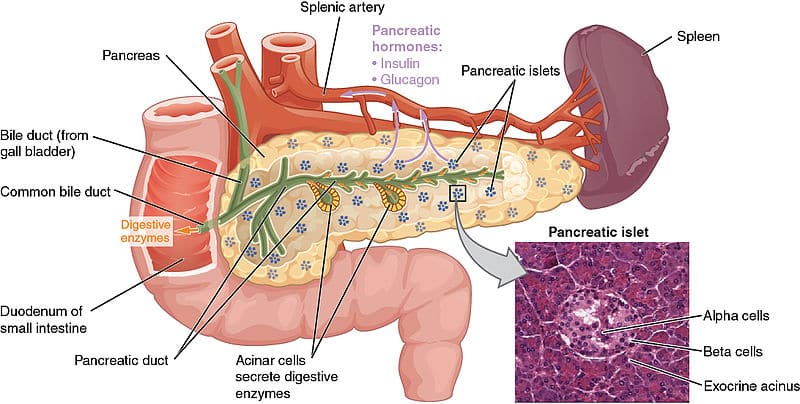
The pancreas plays a crucial role in the digestive system by secreting digestive fluids that are essential for breaking down food. It has both exocrine and endocrine functions, which make it an integral component of digestion and metabolism.
-
Exocrine Function: The pancreas produces digestive enzymes and bicarbonate-rich fluids that are secreted into the small intestine. These enzymes include amylase (for carbohydrates), lipase (for fats), and proteases (for proteins). The bicarbonate neutralizes stomach acid, creating an optimal environment for these enzymes to function effectively. On average, the pancreas secretes about 1.5 to 2 liters of these digestive juices daily. This process is essential for the complete digestion of nutrients contained in the food we consume.
-
Endocrine Function: Besides its digestive role, the pancreas also has endocrine functions where it secretes hormones like insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream. These hormones help regulate blood sugar levels, playing a pivotal role in metabolic processes.
The acinar cells of the pancreas are primarily responsible for the production of digestive fluids, while the islets of Langerhans are responsible for hormone production. The effective functioning of the pancreas is vital for digestion and the maintenance of energy balance in the body.
For more detailed information about the pancreas and its functions, you may refer to the links below:
- Cleveland Clinic: Pancreas Function and Location
- Columbia Surgery: Pancreas Functions and Disease
- InformedHealth.org: How the Pancreas Works
- Osmosis: Pancreatic Secretion
- MUSC Health: Understanding the Pancreas
- ScienceDirect: Overview of Pancreatic Secretion
- Medical News Today: Learning About the Pancreas
In summary, the pancreas is a multifunctional organ that is essential for both digestion and hormonal regulation, highlighting its importance in the body's overall functioning.
Sources

Related Questions
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.
