parenchya of the lung
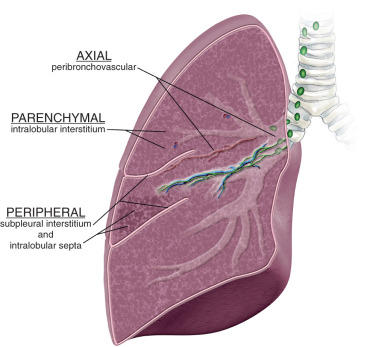
The lung parenchyma is a critical component of the lungs, primarily responsible for gas exchange. Comprising millions of interdependent alveoli, this structure ensures efficient oxygen and carbon dioxide transfer. The alveoli, which are thin-walled air sacs, create a vast surface area that facilitates this exchange, contributing to maintaining adequate levels of oxygenation in the blood.
Lung parenchyma includes not only the alveoli but also associated structures such as respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and terminal bronchioles. This comprehensive definition emphasizes the significance of these components in respiratory physiology. Moreover, the parenchyma is characterized by its ability to prevent overdistension during inhalation, which is crucial for maintaining lung function and health.
Research has also highlighted the biomechanics of lung parenchyma, particularly the roles of collagen and other structural proteins, which support the lung's mechanical properties and functional capabilities. Understanding these mechanics is vital for appreciating how the lungs respond to various physiological demands and pathologies.
For further detailed readings, you can explore resources such as:
- Lung Parenchyma - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
- Lung parenchymal mechanics - PubMed
- Lung parenchyma | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org
- Lung Parenchyma - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics (alternative)
- Lung parenchyma – Knowledge and References - Taylor & Francis
- Biomechanics of the lung parenchyma: critical roles of collagen and ...
- Parenchyma | anatomy - Britannica
These references offer a wealth of knowledge regarding lung parenchyma and its importance in respiratory health.
Sources

Related Questions
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.
