oral finasteride + oral minoxidil vs topical head to head
When comparing oral finasteride and oral minoxidil to their topical counterparts, several studies highlight key differences in their effectiveness and safety profiles.
-
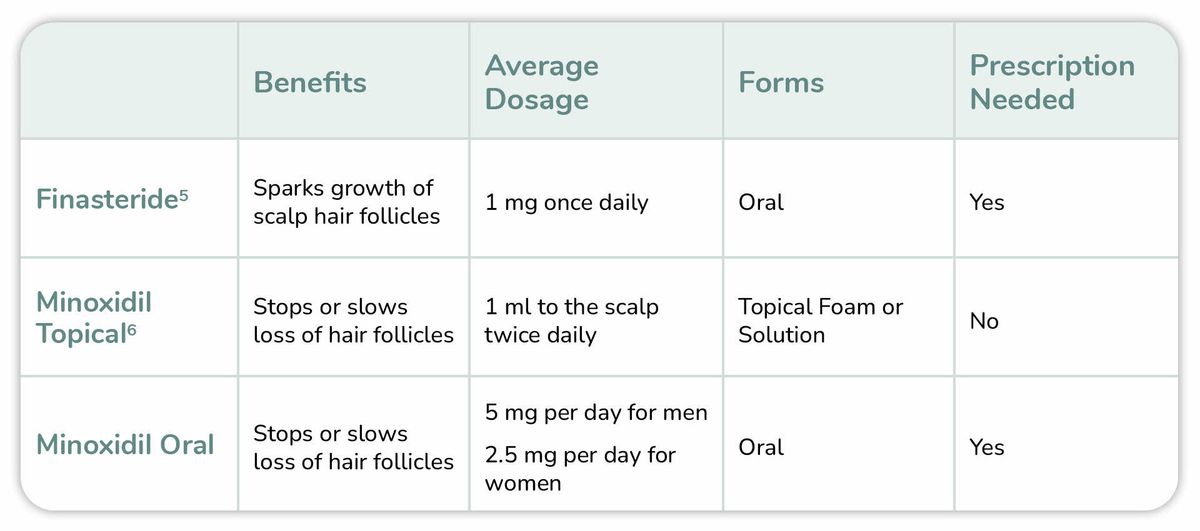
Effectiveness: Research indicates that oral finasteride tends to be more effective than both oral and topical minoxidil in treating hair loss. One study concluded that while both treatments are effective, oral finasteride ranks higher in terms of efficacy compared to topical minoxidil. This finding is supported by another source which stated that finasteride generally outperforms minoxidil in long-term studies regarding hair regrowth.
-
Mechanism of Action: Oral finasteride works by lowering dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels throughout the body, which is a key factor in male pattern baldness. In contrast, topical minoxidil acts as a vasodilator and is applied directly to the scalp to promote hair growth locally.
-
Side Effects: The systemic absorption of oral finasteride can lead to side effects that affect the whole body, whereas topical minoxidil is less likely to cause such widespread effects. Most side effects of topical minoxidil are localized to the site of application.
-
Monotherapy Effectiveness: Studies suggest that, when considering monotherapy treatments, oral finasteride is more effective than topical minoxidil. However, there are indications that oral minoxidil may outperform lower doses of finasteride in certain contexts.
-
Summary of Comparisons: An overview of multiple studies indicates that while both treatments have their merits, oral finasteride is generally considered more effective in the treatment of hair loss than oral or topical minoxidil.
For further reading, you can explore these links for comprehensive insights: PubMed Study, Miiskin Comparison, and GoodRx Differences.In comparing oral finasteride and oral minoxidil versus their topical counterparts for hair loss treatment, various studies and articles provide insightful data regarding their efficacy and side effects.
Efficacy: Research indicates that oral finasteride is generally more effective than both oral and topical minoxidil for promoting hair growth. A study noted that oral finasteride ranks higher in effectiveness than both topical forms of minoxidil and finasteride, although more studies are needed for conclusive evidence (source: PubMed). Other articles corroborate this claim, suggesting that finasteride and minoxidil serve distinct functions; finasteride works by reducing dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels while minoxidil increases blood flow to the hair follicles (source: Miiskin). A long-term comparison also showed finasteride outperforming minoxidil when used alone (source: XYON).
Side Effects: Side effects vary significantly between the two medications. Oral finasteride is associated with more systemic side effects, particularly sexual dysfunction (including decreased libido and erectile dysfunction) (source: GoodRx). In contrast, topical minoxidil tends to cause localized side effects such as scalp dryness and irritation (source: Dr. Michele Green). Oral minoxidil may also lead to hypertrichosis (excessive hair growth) and cardiovascular symptoms (source: PubMed).
In summary, while oral finasteride may offer superior hair growth results, it carries a higher risk of significant side effects, particularly relating to sexual health. Topical minoxidil, although effective, mainly leads to localized adverse effects. Each treatment has its specific advantages and drawbacks, and the choice between them should align with individual preferences and tolerance to possible side effects.
Sources

Related Questions
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.
