Menometrorrhagia (when menstrual bleeding occurs outside the monthly cycle or
Menometrorrhagia refers to a condition characterized by menstrual bleeding that occurs outside the regular monthly cycle, often involving extremely heavy and/or prolonged periods. This can result in various complications, such as anemia due to significant blood loss. Women experiencing menometrorrhagia may also encounter pelvic pain and pressure, along with chronic discomfort in the lower abdominal area. Often, this condition is associated with the presence of large uterine myomas (fibroids), which can contribute to pelvic pressure and pain.
In addition to these symptoms, there is a concern regarding enlarging fibroids that may have the potential for malignancy, emphasizing the importance of monitoring and medical evaluation. Obstruction of the ureters is another possible complication associated with substantial uterine fibroids, which may lead to further discomfort and urinary issues.
For those seeking information on menometrorrhagia, several resources discuss its causes and treatment options:
-
Mayo Clinic provides an overview of symptoms and causes of heavy menstrual bleeding, which can be categorized under menorrhagia, detailing the clinical aspects and implications of the condition. Visit Mayo Clinic.
-
WebMD outlines various causes of menometrorrhagia and highlights that surgical intervention may be necessary depending on the underlying cause. Read more on WebMD.
-
Healthline discusses treatment options for menometrorrhagia, recommending surgical removal of fibroids or a hysterectomy in certain cases. Explore Healthline.
-
Another article from Mayo Clinic delves deeper into the diagnosis and treatment of heavy menstrual periods, shedding light on various management strategies. Learn more here.
-
Johns Hopkins Medicine explains menorrhagia as heavy or prolonged bleeding linked to hormonal issues or uterine problems, which may require significant medical intervention. Visit Johns Hopkins.
-
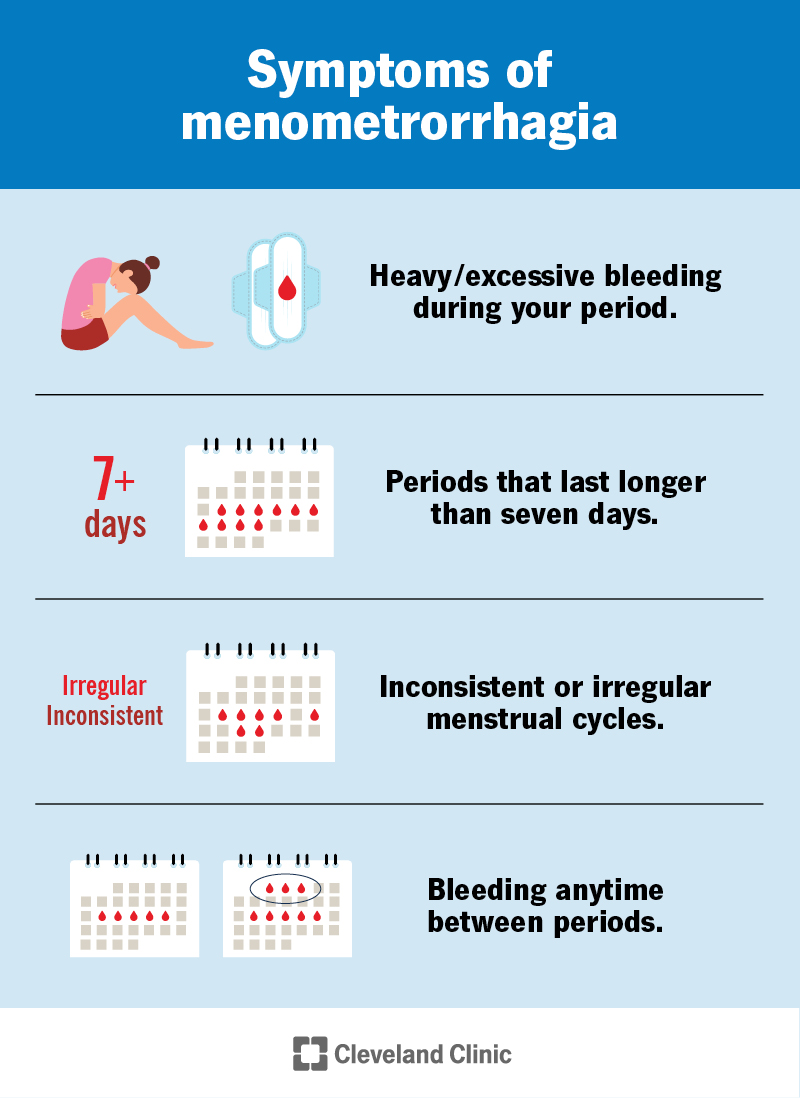
Cleveland Clinic provides a detailed account of menorrhagia, noting that prolonged bleeding beyond seven days or frequent pad changes could indicate its presence. More on Cleveland Clinic.
-
Lastly, StatPearls offers insights on the first-line treatments for abnormal uterine bleeding, emphasizing hormonal therapy as a primary intervention. Refer to StatPearls.
These resources offer valuable insights for understanding menometrorrhagia, its symptoms, complications, and management options.
Sources

Related Questions
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.
