How Do You Think The Average Meat Consumption Has Changed
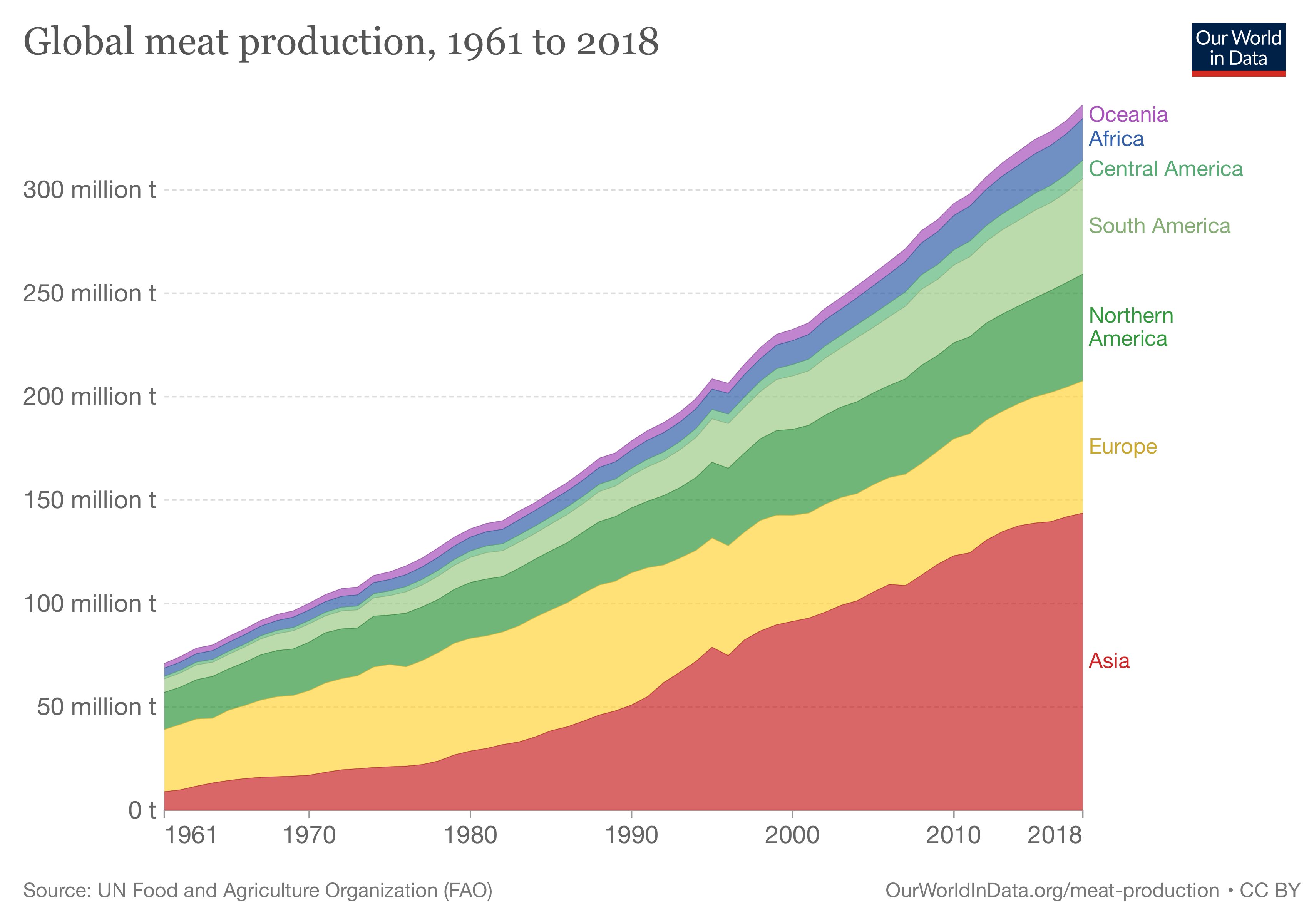
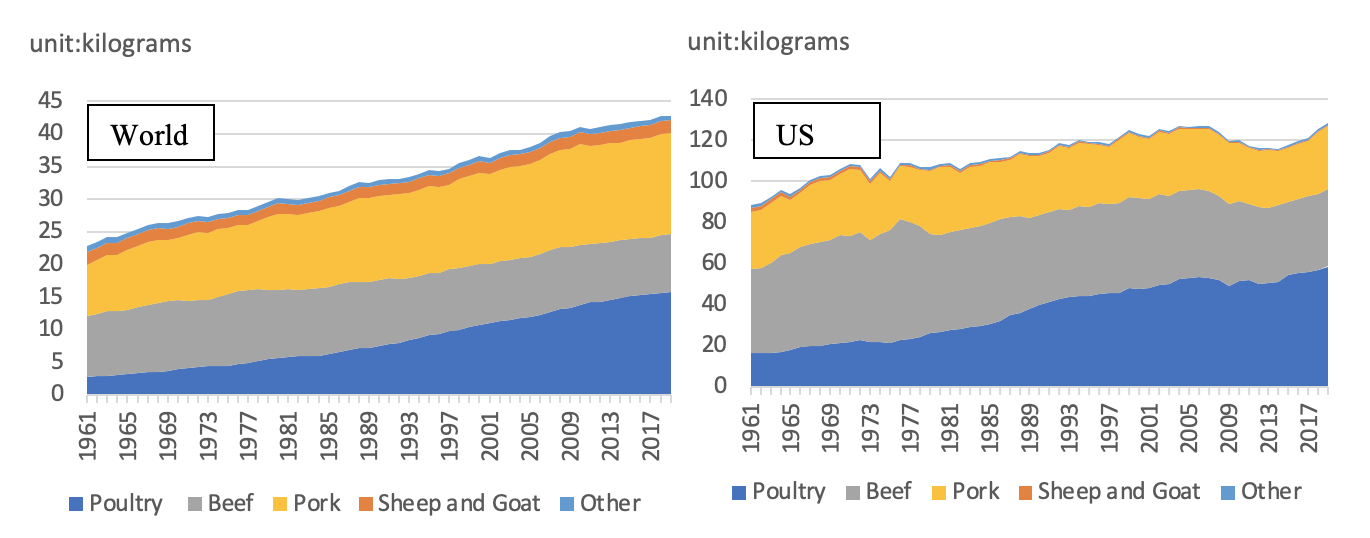
Over the last 50 years, global meat consumption has risen significantly due to economic development, urbanization, and a shift towards animal-based protein (ABP) consumption. This trend has led to negative environmental impacts, such as increased carbon dioxide emissions and other factors associated with climate change. The rise in meat consumption is expected to continue, particularly in the U.S., where it is projected to increase by 1 percent each year through 2023. This has raised health and moral concerns, and calls for a shift towards healthier diets and plant-based foods to reduce the environmental and climate footprints associated with meat production.
The average meat consumption has increased significantly over the last 50 years due to economic development, urbanization, and a growing preference for animal-based protein (ABP) diets. This shift has led to negative environmental impacts, including increased carbon dioxide emissions and other factors associated with climate change. The rising meat consumption is expected to continue, particularly in the U.S., where it is projected to increase by 1 percent annually through 2023. This has prompted calls for a shift towards healthier diets and plant-based foods to reduce the environmental and climate footprints associated with meat production. One noticeable difference lies in the hectares of land required for meat production compared to non-meat products, with meat production generally requiring more land and resources, contributing to environmental pressures such as deforestation and habitat loss.
Sources
Related Questions
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.
