how are epoxy resins manufactured
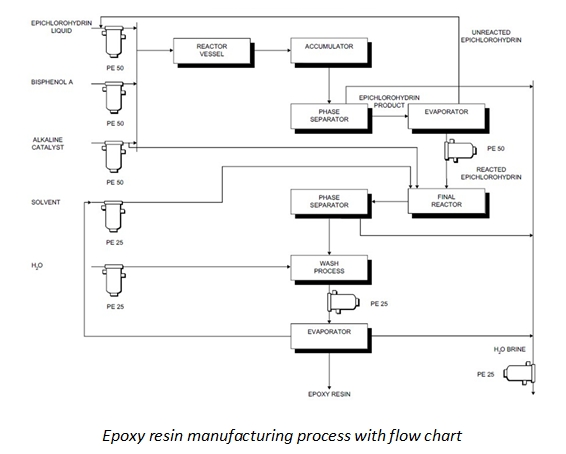
Epoxy resins are commonly produced through a chemical reaction between two primary components: epichlorohydrin (ECH) and bisphenol-A (BPA). This process involves the following steps:
-
Raw Material Selection: Traditionally, the production of epoxy resins relies heavily on petroleum-derived raw materials. However, newer formulations are beginning to incorporate plant-derived sources as well, reflecting a growing trend towards more sustainable manufacturing practices.
-
Chemical Reaction: The key reaction in creating epoxy resins is between ECH and BPA. During this reaction, the epoxide groups formed are critical for the curing process, enabling the resin to harden into a stable thermosetting polymer.
-
Polymerization Process: Once the reaction takes place, the mixture undergoes polymerization, where the resulting epoxy resin is formed as long chains of molecules that characterize its excellent adhesion, chemical resistance, and mechanical properties.
-
Formulation and Additives: Manufacturers may enhance the properties of the epoxy resin by adding various additives or formulations, tailoring it for specific applications such as coatings, adhesives, and composite materials. Adjustments may be made based on the desired performance characteristics.
For more detailed insights into the manufacturing process of epoxy resins, you can refer to articles such as "Epoxy: Manufacturing Process & Applications" here and additional information available on Wikipedia here.
In summary, epoxy resin manufacturing is largely centered around the reaction between ECH and BPA, with ongoing advancements beginning to incorporate more sustainable plant-based materials into the process. This evolution not only caters to performance needs but also addresses environmental concerns surrounding traditional petroleum dependence.
Sources

Related Questions
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.
