Describe the mechanism of action, and adverse effects of nitrofurantoin
Mechanism of Action of Nitrofurantoin
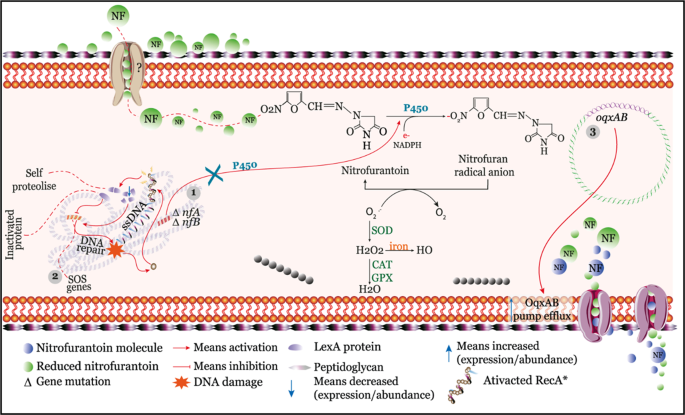
Nitrofurantoin is an antibiotic primarily used for treating uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections. Its mechanism of action involves a multi-step biochemical process that takes place within bacterial cells. When nitrofurantoin enters these cells, it undergoes reduction by bacterial flavoproteins, resulting in the formation of reactive intermediates. These intermediates play a key role in nitrofurantoin's antibacterial activity (source: StatPearls, Medsafe).
The activated forms of nitrofurantoin can inactivate various macromolecules, including ribosomal proteins, disrupting protein synthesis and ultimately impairing bacterial growth. While nitrofurantoin typically inhibits bacterial growth (bacteriostatic effect), it may also kill bacteria (bactericidal effect) at higher concentrations found in urine (source: Wikipedia, ScienceDirect Topics).
Adverse Effects of Nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantoin can cause a range of side effects, including both common and more serious reactions:
-
Common Side Effects:
- Gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are among the most frequently reported effects (source: Mayo Clinic).
- Dark yellow or brown urine, a benign effect due to the drug's metabolites (source: NHS).
-
Serious Side Effects:
- Allergic reactions that may manifest as rashes, itching, swelling of the face, lips, or throat, and difficulty breathing (source: MedlinePlus).
- Pulmonary complications such as cough, shortness of breath, or chest pain, which may indicate serious lung issues, particularly in those with existing conditions or prolonged use (source: GoodRx).
- Hepatotoxicity, with potential liver injury noted through elevated liver function tests (rare).
-
Long-term Effects:
- Prolonged use can lead to antibiotic resistance and may increase the risk of infections caused by non-susceptible organisms (source: Drugs.com).
In conclusion, while nitrofurantoin is effective against urinary tract infections through its unique mechanism centered around reactive intermediate formation, awareness of its side effects, especially in long-term or vulnerable patients, is essential for safe use.
Sources

Related Questions
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.
