Acheson Furnace, How It Work For Synthetic Graphite? qUhQsFT
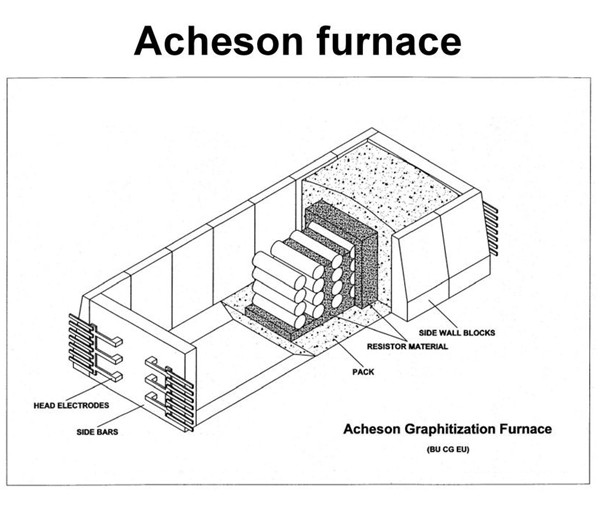
The Acheson Furnace plays a crucial role in the production of synthetic graphite through a process known as the Acheson process. Here’s a detailed explanation of how this furnace works for synthesizing graphite from petroleum coke (petcoke):
Overview of the Acheson Process
The Acheson process involves heating carbonaceous materials (like petcoke) to extremely high temperatures using a specialized electric furnace. This process results in the conversion of non-graphitic carbon into a high-purity graphite form.
Working Principle of the Acheson Furnace
-
Preparation of Feed Material:
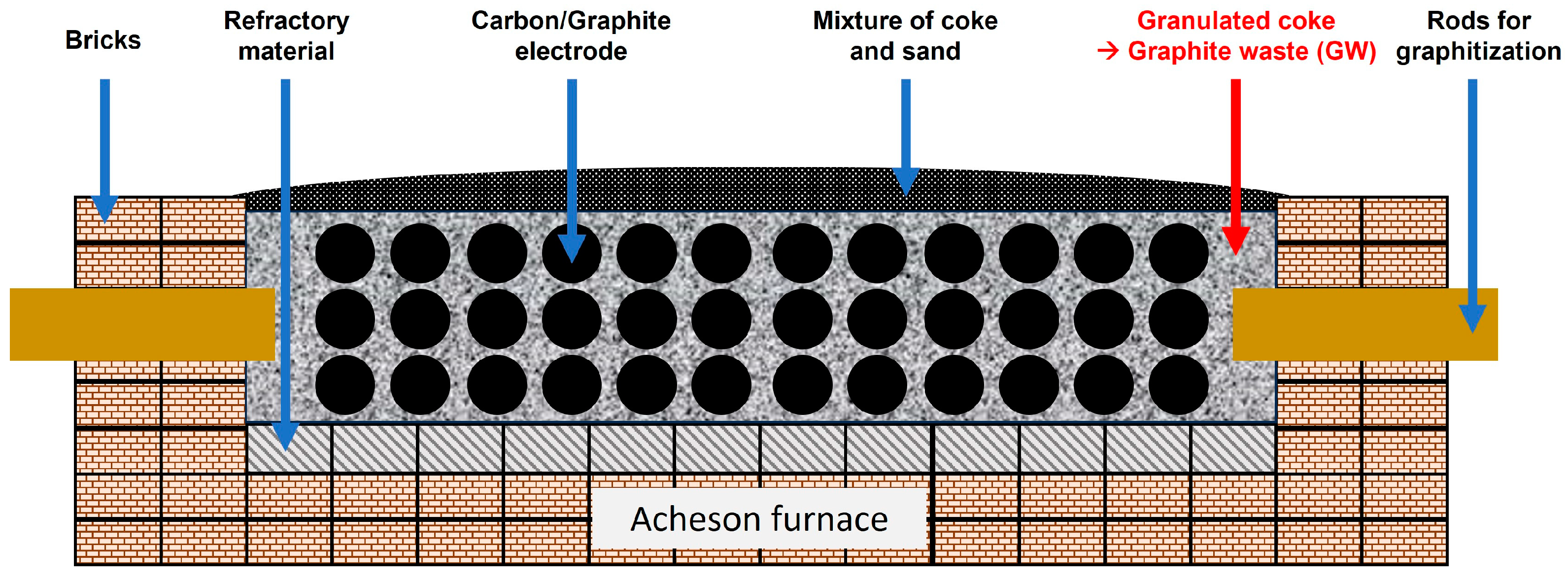
- Petroleum Coke: Initially, quality petroleum coke is selected. This material is a byproduct from the oil refining process and contains amorphous carbon which needs to be converted into graphite.
- Ground and Shaped: The petcoke is ground to a fine powder and possibly mixed with a binder to form a cohesive mixture, which is then shaped into green electrodes.
-
Charging the Furnace:
- The green electrodes, prepared from the petcoke-binder mix, are placed inside the Acheson furnace. This furnace generally consists of a cylindrical chamber lined with carbon electrodes.
-
Heating and Graphitization:
- High-Temperature Environment: The furnace operates at extremely high temperatures, typically between 2500°C to 3000°C. This is achieved by applying a strong electrical current through the carbon electrodes.
- Thermal Decomposition: As the temperature rises, volatile components are driven off, while the carbon atoms in the petcoke start to reorganize into a more stable graphitic structure.
- Graphitization Reaction: The process involves thermal rearrangement, wherein the disordered carbon atoms in the petcoke transform into a crystalline graphite structure over time.
-
Cooling Phase:
- Once the graphitization is complete, the furnace is allowed to cool gradually. This controlled cooling is essential to prevent defects in the synthetic graphite structure.
-
Extraction and Further Processing:
- After cooling, the synthetic graphite is extracted from the furnace. It may undergo further processing, including crushing, milling, and purification, to achieve the desired characteristics and particle size for various applications.
Applications of Synthetic Graphite
The synthetic graphite produced via the Acheson process finds extensive applications across industries:
- Electrodes: Used in electric arc furnaces for steel manufacturing.
- Batteries: Serves as a key component in lithium-ion batteries.
- Lubricants: Acts as a lubricant in various mechanical applications.
Key Advantages
The Acheson furnace is preferred for its ability to produce high-purity synthetic graphite efficiently. Moreover, the process is well-established, making it a cornerstone in graphite manufacturing techniques.
For more detailed technical insights about the Acheson process, you can refer to the relevant resources such as this comprehensive overview and additional studies available on graphitization practices.
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.