Abnormal Involantory Movment Objective Assesment Tools?
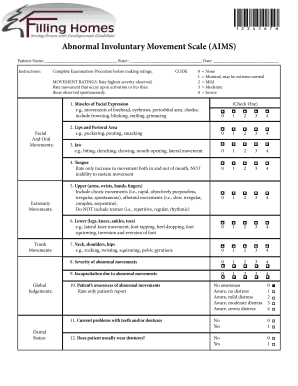
For the objective assessment of abnormal involuntary movements, particularly those associated with tardive dyskinesia (TD), several resources are available, predominantly focusing on the Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS). This scale is designed to quantitatively evaluate the severity of involuntary movements in affected individuals.
-
Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS) - AACAP: This PDF provides detailed guidelines on how to use the AIMS for clinical assessments, including movement ratings and considerations for different severity levels. It emphasizes the importance of judging movements that surface with activity as slightly less severe than those occurring spontaneously. You can access this resource here.
-
Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS) - MDCalc: This tool specifically measures the involuntary movements indicative of tardive dyskinesia, providing a structured approach for calculating the scale scores. More information can be found on the MDCalc site here.
-
AIMS Overview - NP Psych Navigator: This resource introduces the AIMS as a 12-item, clinician-rated scale specifically focusing on the severity of tardive dyskinesia in patients with relevant treatment backgrounds. Access the full details here.
-
AIMS Assessment and Training - aapp.org: This site offers interactive sessions aimed at training clinicians to appropriately administer the AIMS assessment. It is accredited and focuses on best practices. More about these sessions can be found here.
-
AIMS on Medscape: A thorough overview of the AIMS and its role in monitoring abnormal movements over time is provided on Medscape. This site explains how clinicians can track movements following medication administration. Access this detailed description here.
-
Comprehensive PDF - AIMS: Another PDF version of the AIMS outlines how to conduct the assessment, including a hands-on component where patients tap their thumbs with fingers in a timed manner. This document can be accessed here.
-
AIMS Document - Missouri DMH: This document outlines the use of the AIMS not only for detection but also for tracking the severity of tardive dyskinesia over time, highlighting its importance in clinical practice. You can read more here.
These resources collectively provide a robust framework for assessing and monitoring abnormal involuntary movements, with the AIMS serving as a key tool in clinical settings.
Sources

Related Questions
Work fast from anywhere
Stay up to date and move work forward with BrutusAI on macOS/iOS/web & android. Download the app today.
